Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What is CUDA
What is a GPU
Objectives
Learn what CUDA is used for
Learn about computer architecture
A brief history of GPU computing
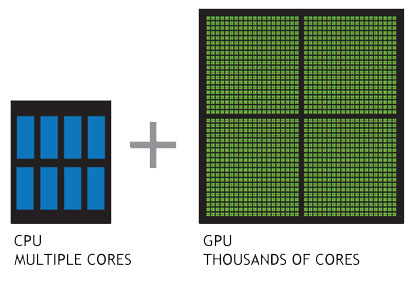
Multi-core central processing units (CPUs)
CPUs are general purpose processors, optimised for serial tasks, branching operations and file operations.
Almost all consumer PCs and laptops have central processing units (CPUs) with multiple cores. Many mobile phones and tablets have multiple core CPUs too. The reason for multiple cores is that manufacturers have been unable to increase performance by increasing clock speed (clock speed measures the rate at which calculations can be performed, i.e. how quickly a CPU is able to execute instructions).
Graphics processing units (GPUs)
GPUs are special purpose processors, optimised to do floating point arithmetic, especially SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) operations.
The development of GPUs has been driven by the 3D graphics requirements of the games industry, but the calculations they are optimised for (linear algebra matrix operations) also happen to be the type of calculation required for most computationally expensive scientific problems.
Graphics cards are massively parallel processors, (typically 2000-3000 cores). Each core is less powerful than a typical CPU, but GPU cores are special purpose processors and there are lots of them on a GPU card, so speed increases of 10 – 1000+ times are possible.
What is CUDA?
Compute Unified Device Architecture, a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API), created by Nvidia.
CUDA can be used to leverage the parallel processing capabilities of Nvidia GPUs. There are three basic approaches to CUDA usage:
- using CUDA-accelerated libraries (a library is a collection of pre-compiled functions)
- adding compiler directives (“hints” to auto-parallelisze your code)
- using extensions to standard programming languages e.g. C, Fortran, that can run sections of code on the GPU (there is no requirement to learn a new “GPU programming language”!).
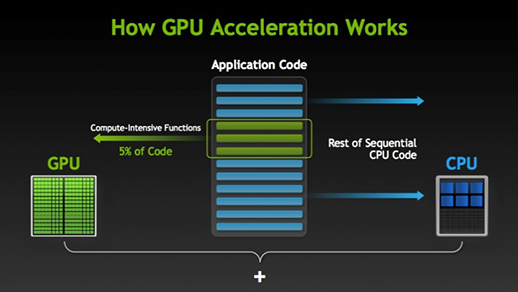
CUDA programming is a hybrid model where serial sections of code run on the CPU and parallel sections run on the GPU.
Types of parallelism
The hybrid nature of CUDA means that computation on the CPU can overlap with computation on the GPU.
Far greater parallelism occurs within the GPU itself, where subroutines are executed by many threads in parallel. These threads execute the same code, but on different data. For example adjacent threads may operate on adjacent data such as elements of an array.
Contrast with a model like Message Passing Interface (MPI) where the data is split into portions and each MPI process (on a separate CPU) performs calculations on an entire data segment.
GPU vs CPU analogy
Key Points
CUDA is used for parallel programming on Nvidia GPU cards